|
 

 |
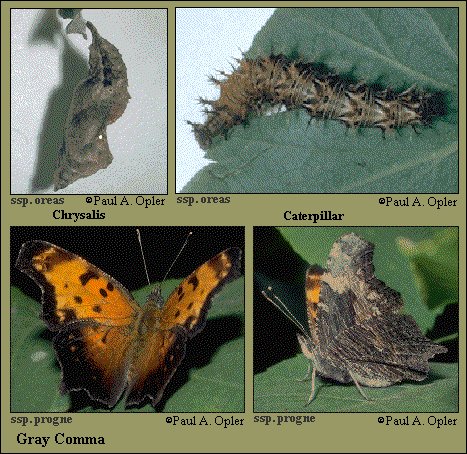



Gray comma (Polygonia progne [Cramer])
Wing span: 1 5/8 - 2 /12 inches (4.4 - 6.3 cm).
Identification: Upperside is bright orange-brown; summer form has hindwing with a wide dark border, winter form has the border covering only about 1/4 of the wing; both enclosing a few small yellow spots. Underside is charcoal gray with fine dark striations; forewing with 3-4 light chevrons in a dark border. Silver mark in center of hindwing is small, slender, and L-shaped.
Life history: In midafternoon, males perch on trees or shrubs at the edges of clearings to wait for females. Eggs are laid singly on leaves of host plants; the caterpillars feed underneath. Adults overwinter.
Flight: Two flights: In April and May the winter form emerges from hibernation, mates, and lays eggs which develop into the summer generation. Summer adults fly from June-August, laying eggs of the winter generation which appears in October and then hibernates.
Caterpillar hosts: Gooseberries (Ribes) and azalea (Rhododendron).
Adult food: Sap; rarely flower nectar.
Habitat:Along dirt roads, along streamsides, and within clearings in rich deciduous or confierous woods, in aspen parks, yards, and gardens. Often in hilly terrain or canyons.
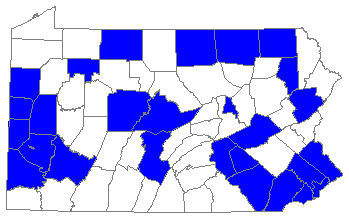
Range: Northwest Territories and British Columbia south along Pacific coast to central California, southeast through Montana, Utah, Colorado, and the Dakotas to eastern Nebraska, central Kansas, and central Arkansas; east through southern Canada and the northern United States to Maine and the Maritimes; south in the Appalachians to North Carolina.
Conservation: Not usually required.
The Nature Conservancy Global Rank: G5 - Demonstrably secure globally, though it may be quite rare in parts of its range, especially at the periphery.
Management needs: None reported.
Note: The Gray Comma includes Polygonia oreas and its subspecies silenus and nigrozephyrus. These were previously treated as a separate species.
References:
Opler, P. A. and G. O. Krizek. 1984. Butterflies east of the Great Plains. Johns
Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. 294 pages, 54 color plates.
Opler, P. A. and V. Malikul. 1992. A field guide to eastern butterflies. Peterson
field guide #4. Houghton-Mifflin Co., Boston. 396 pages, 48 color plates.
Scott, J. A. 1986. The butterflies of North America. Stanford University Press,
Stanford, Calif. 583 pages, 64 color plates.
Tilden, J. W. 1986. A field guide to western butterflies. Houghton-Mifflin Co.,
Boston, Mass. 370 pages, 23 color plates.
Author: Jane M. Struttmann
State and Regional References:
Glassberg, J. 1993. Butterflies Through Binoculars: A Field Guide to
Butterflies in the Boston-New York-Washington Region. Oxford Univ. Press,
New York, N.Y. 160 pp.
Layberry, R.A., Hall, P.W. & Lafontaine, D.J., 1998. The Butterflies of
Canada. University of Toronto Press, Toronto, ON. 280 pp.
Opler, P.A. 1998. A field guide to eastern butterflies, revised format.
Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston.
Shapiro, A.M. 1966. Butterflies of the Delaware Valley. American Entomological
Society Special Publication. Philadelphia, PA. 79 pp.
Tietz, H.M. 1952. The Lepidoptera of Pennsylvania. The Pennsylvania State
College School of Agriculture Agricultural Experiment Station. State
College, PA. 194 pp.
Wright, D.M. 1995, Atlas of Pennsylvania Butterflies. Special Private
Publication, Lansdale, PA. 22 pp.