|
 

 |



Red Admiral (Vanessa atalanta [Linnaeus])
Wing span: 1 3/4 - 3 inches (4.5 - 7.6 cm).
Identification: Upperside is black with white spots near the apex; forewing with red median band, hindwing with red marginal band. The winter form is smaller and duller, summer form larger and brighter with an interrupted forewing band.
Life history: The Red Admiral has a very erratic, rapid flight. Males perch, on ridgetops if available, in the afternoon to wait for females, who lay eggs singly on the tops of host plant leaves. Young caterpillars eat and live within a shelter of folded leaves; older caterpillars make a nest of leaves tied together with silk. Adults hibernate.
Flight: Two broods from March-October in the north, winters from October-March in South Texas.
Caterpillar hosts: Plants of the nettle family (Urticaceae) including stinging nettle (Urtica dioica), tall wild nettle (U. gracilis), wood nettle (Laportea canadensis), false nettle (Boehmeria cylindrica), pellitory (Parietoria pennsylvanica), mamaki (Pipturus albidus), and possibly hops (Humulus).
Adult food: Red Admirals prefer sap flows on trees, fermenting fruit, and bird droppings; visiting flowers only when these are not available. Then they will nectar at common milkweed, red clover, aster, and alfalfa, among others.
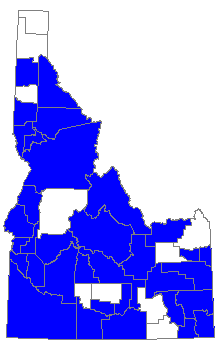
Habitat: Moist woods, yards, parks, marshes, seeps, moist fields. During migrations, the Red Admiral is found in almost any habitat from tundra to subtropics.
Range: Guatemala north through Mexico and the United States to northern Canada; Hawaii, some Caribbean Islands, New Zealand, Europe, Northern Africa, Asia. Cannot survive coldest winters; most of North America must be recolonized each spring by southern migrants.
Conservation: Not required.
The Nature Conservancy Global Rank: G5 - Demonstrably secure globally, though it may be quite rare in parts of its range, especially at the periphery.
Management needs: None reported.
References:
Opler, P. A. and G. O. Krizek. 1984. Butterflies east of the Great Plains. Johns
Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. 294 pages, 54 color plates.
Opler, P. A. and V. Malikul. 1992. A field guide to eastern butterflies. Peterson
field guide #4. Houghton-Mifflin Co., Boston. 396 pages, 48 color plates.
Scott, J. A. 1986. The butterflies of North America. Stanford University Press,
Stanford, Calif. 583 pages, 64 color plates.
Tilden, J. W. 1986. A field guide to western butterflies. Houghton-Mifflin Co.,
Boston, Mass. 370 pages, 23 color plates.
Author: Jane M. Struttmann
State and Regional References:
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown. 1980. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountain States.
University of Oklahoma Press. Norman.
Layberry, R.A., Hall, P.W. & Lafontaine, D.J., 1998. The Butterflies of
Canada. University of Toronto Press, Toronto, ON. 280 pp.
Opler, Paul A. 1999. Peterson Field Guide to Western Butterflies, revised
edition. Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston, Mass.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of Western USA Butterflies.
Privately published, Denver, Colo.
Tilden, J.W. and A.C. Smith. 1986. A Field Guide to Western Butterflies.
Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston, Mass.